How to use command prompt to identify and solve problems in your Broadband internet connection on Windows
How to use command prompt to identify and solve problems in your Broadband internet connection
The command prompt. A forgotten and often under-estimated software of
the Windows ecosystem. As a regular reader would know by now, the
command prompt has a long lists of uses that tend to get ignored by the
uninitiated. One aspect of these uses that we’ll see today is to test
and improve one’s internet connection.
Using Ping
First thing to test, is your internet connection. We do this, by
using Ping. Ping is a Windows program that comes pre-installed with the
OS. It is a text based program and therefore needs text based commands
to execute. It’s the software used to test the latency on your
connection. For those who don’t know, latency is the time taken to
establish a connection between your computer and the web server hosting
the website you requested.
The first thing to do, is open the Start Menu and search for the
command prompt. You can do this by typing “cmd” in the search box and
hitting enter. Once you have the command prompt open, you can use Ping
to test your connection. Enter the command ping google.com.
Once typed, hit Enter and wait for your command prompt to look like
the image below. Do note, that the results are not displayed instantly,
so you might have to wait a while for the results to pop up.
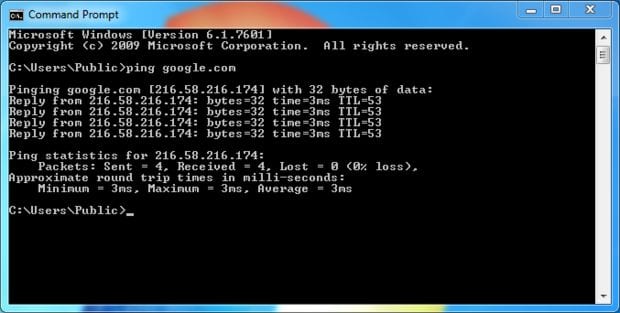
Understanding the results
- Sent – the number of packets sent to the address; default value of 4
- Received – number of packets received from the web address; ideally same as the number of packets sent.
- Lost – number of packets that did not return from the server back to you; ideally zero
- Minimum – the minimum time it took for the packet you sent to return back to you (in milliseconds)
- Maximum – the longest time it took a packet to make the round trip (in milliseconds)
- Average – this is the average time the packets took and therefore, the lower the average, the better is your connection. An average time of 3 ms is considered very good.
What matters to us however, is an unusually higher time taken for the
round trip or a large number of packet loss. If this happens, it can
point to some issues in your internet connection. If its a
physical/hardware issue, it is time to have it checked out. If however,
that’s not the case then you could try the following steps to boost the
speed. While it might not always resolve the issue, at times, users do
not get the maximum speed possible from their ISPs.
The following steps
also use the command prompt and will help you resolve the issue, if it
exists.
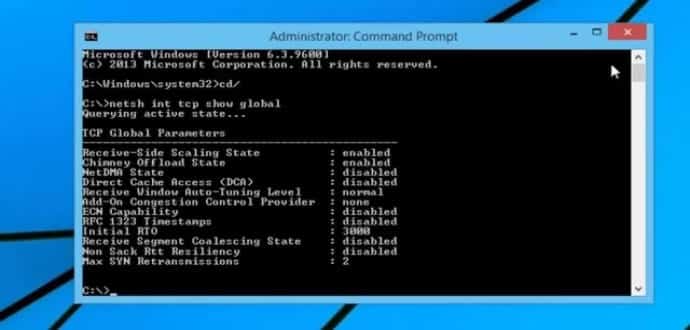
Step 1: Open the command prompt in the way already discussed and type netsh int tcp show global and hit enter.
Step 2: The next step is to change the default TCP parameters. Open your notepad and enter the following lines
cd\netsh int tcp show globalnetsh int tcp set global chimney=enablednetsh int tcp set heuristics disablednetsh int tcp set global autotuninglevel=normalnetsh int tcp set global congestionprovider=ctcp
Step 3: Save this file with the name Boostspeed.bat
Step 4: Run this file in administrator mode and once the changes take
effect, you should notice an increase in your internet speed. Users
have reported an increase of upto 35% at times after these steps.
Hopefully they might work for you as well.
Step 5: Just in case you wish to revert back to the default TCP
parameters or have the option to revert back if ever needed, you can
save the following lines in another .bat file.
cd\netsh int tcp show globalnetsh int tcp set global chimney=defaultnetsh int tcp set heuristics enablednetsh int tcp set global congestionprovider=none
Source: Instructables